
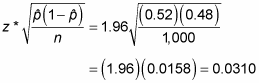
It is one of an important & most frequently used functions in statistics & probability. In other words, it's a numerical value that represents standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic for sample mean x̄ or proportion p, difference between two sample means (x̄ 1 - x̄ 2) or proportions (p 1 - p 2) (using either standard deviation or p value) in statistical surveys & experiments. It shows how effective the selected sample size n is in the statistical experiments or the reliability of experiment results with respect to the sample size. (0.7731, 0.8269) We estimate with 90% confidence that the true percent of all students in the district who are against the new legislation is between 77.31% and 82.69%.In probability & statistics, the standard deviation of sampling distribution of a statistic is called as Standard Error often abbreviated as SE.

Compute a 97% confidence interval for the true percent of students who own an iPod and a smartphone.
How do you know you are dealing with a proportion problem? First, the underlying distribution is a binomial distribution. The procedure to find the confidence interval, the sample size, the error bound, and the confidence level for a proportion is similar to that for the population mean, but the formulas are different. Confidence intervals can be calculated for the true proportion of stocks that go up or down each week and for the true proportion of households in the United States that own personal computers. Businesses that sell personal computers are interested in the proportion of households in the United States that own personal computers. Investors in the stock market are interested in the true proportion of stocks that go up and down each week. Often, election polls are calculated with 95% confidence, so, the pollsters would be 95% confident that the true proportion of voters who favored the candidate would be between 0.37 and 0.43: (0.40 – 0.03,0.40 + 0.03). For example, a poll for a particular candidate running for president might show that the candidate has 40% of the vote within three percentage points (if the sample is large enough). Calculate the sample size required to estimate a population mean and a population proportion given a desired confidence level and margin of errorĭuring an election year, we see articles in the newspaper that state confidence intervals in terms of proportions or percentages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
